The March 2018 United States Joint Economic Committee Report officially endorses the future of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency in the U.S. Chapter 9 of the report discusses blockchain, and is titled “Building a Secure Future, One Blockchain at a Time.” Chapter 9 begins by saying Blockchain is “not only nearly invulnerable to cyberattack but is revolutionizing the way the world conducts commerce and shares information.”
In the report’s general opening, Congress acknowledges, “it is important to proceed with prudence and provide proper guidance to the market… and not prejudge or hinder technological developments.” They continue, “The new technology also may be attractive for Government to use, improving efficiency in its own operations.” See p. 20-21. It appears Congress is looking to regulate Blockchain in a way that allows technological innovation to flourish and become integrated with already existing markets. That is incredible news for the future of crypto and blockchain in the U.S.
Congress sees valuable uses for blockchain in the medical sector. The report acknowledges that blockchain could help coordinate health records by reducing paperwork burdens and preventing medical errors. p. 22. It also acknowledges blockchain technology could provide powerful solutions for portability, enabling medical records to be carried on smartphones and mobile devices with very little risks of vulnerability to cyberattacks. p. 198.
Congress sees Blockchain’s revolutionary uses for enabling global economic participation. The report views blockhain as “a secure transmission and recordkeeping technology in its infancy with vast potential to revolutionize the forms in which we transact and document commercial activity of virtually any kind around the world.” p. 166.
The Ch. 9 report lays out three main points about blockchain. p. 201
Blockchain is a potential tool for securing America’s digital infrastructure, protecting against economic losses, cyberattacks, and threats. Blockchain technology became mainstream in 2017, and provides both cybersecurity and many other potential benefits. Blockchain technology could revolutionize the world’s digital landscape and economy. Blockchain innovations and markets present U.S. institutions with unique regulatory challenges.
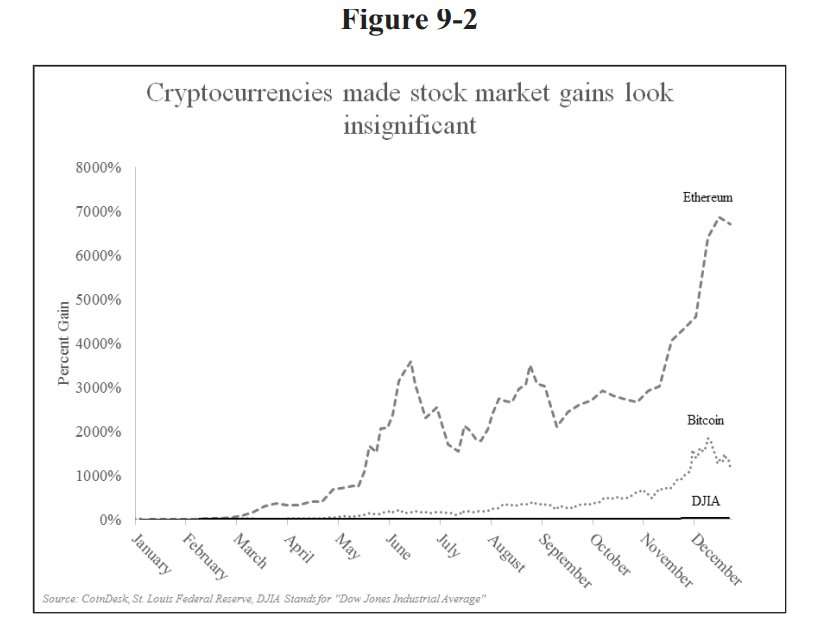
The report calls 2017 “The Year of Cryptocurrencies.” It shows how “Bitcoin” searches skyrocketed, while “blockchain” and “Ethereum” moved out of relative obscurity. The report also shows how the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) grew over 24% and the S&P grew over 17%, but that cryptocurrency growth made stock market gains seem meager in comparison. p 202-203
Pages 205-207 impressively and accurately define blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. “Blockchain is the distributed ledger technology that underlies digital currencies such as Bitcoin. A ledger is the accounting tool that tracks the movement of money from one person or account to another. Conventionally, such records are stored in central locations like banks, headquarters, and Paypal servers. Blockchain revolutionizes ledger technology with a network of distributed ledgers. Instead of one central, authoritative record of all transactions or information, blockchain creates potentially thousands of identical ledgers in computers and servers all over the world.” The definition goes on to define Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus, and discuss the differences and uses of Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Pages 207-209 discuss the challenges cryptocurrencies face to be accepted as actual currency. The report’s conclusion is that cryptocurrencies resemble real assets or commodities more than currencies, though their future role could expand to include functioning as mediums of exchange. Currency must serve three functions: medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value. The report shows Bitcoin’s limitations as a medium of exchange, citing long transaction times and high fees, and further acknowledging that protocol improvements and off-chain solutions could speed up processing times and reduce transaction fees to help move cryptocurrency into the realm of actual currency. The report also mentions that extreme volatility impairs cryptocurrencies’ use as money. Compared to the annual U.S. dollar loss value of about 2% to inflation, cryptocurrency values are much more unpredictable. The report suggests decreasing volatility would help cryptocurrency be used more successfully as actual currency.
Pages 209-212 discuss ICOs and their recent explosion in growth. It acknowledges that “[a]n ICO consolidates two important elements of building a new economic ecosystem, obtaining funding and creating a network.” The report says how ICOs do not offer equity and are much less expensive than an Initial Public Offering (IPO). The report also estimates that most ICO projects will likely fail, as most startups do, but the ones that survive could transform the way the internet and technology works for decades to come.
Pages 212-215 discuss blockchain innovations and uses. The article importantly distinguishes that cryptocurrency headlines often only focus on financial applications but miss the digital revolution with blockchain’s technological applications. The report again mentions how blockchain could be used for health care providers, patients, and policymakers to store medical records digitally and securely. New blockchain products help coordinate payment (healthnexus), monitor and reward patients for following clinical recommendations (RoboMed Network), track pharmaceuticals along the supply chain (MediLedger), identify specific supply chain problems such as those associated with the opioid crisis (BlockMedx), and protect Americans’ private medical data. As a side note, I find the report’s mention of these specific blockchain projects interesting. Maybe the government is considering moving towards adopting and using specific blockchain projects.
The report also mentions that ” [f]rom applications ranging from management of the electrical grid and utilities to how companies manage global supplies, the potential for blockchain is truly revolutionary. Pages 214-215 continue to give examples of blockchain’s technological value.
Pages 215-218 discuss issues with blockchain and cryptocurrency, along with potential misuses. The report acknowledges theft from centralized exchanges as a potential issue, citing Coinbase as a potential vulnerable storage space for cryptocurrency, and using the Mt. Gox exchange hack as a historical example of the risk. The report also mentions that some economists estimate that about 25% of all users conduct illegal transactions on Bitcoin. The report continues to mention how rapid appreciation in value of cryptocurrencies and ICOs contributed to unease about blockchain technology, causing wild volatility and speculative bubbles to arise in the market. The report also mentions DogeCoin as a “warning sign” in the market, because it is a “joke,”, but fails to realize that 1 DOGE always equals 1 DOGE.
Pages 218-225 discuss the future of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain regulations.
The SEC has recently started pursuing more enforcement actions against new tokens for both securities registration issues and fraud. Securities as defined by the Securities Act is a contract, transaction, or scheme whereby a person: 1) invests her/his money in 2) a common enterprise, and is led to 3) expect profits 4) solely from the efforts of the promoter or a third party. Tokens can be classified as securities, but can also be exempt under the definition and qualify instead as utility tokens. Regulations may be needed to further clarify how cryptocurrencies fall under the Securities Act.
The report acknowledges that questions remain about how to tax cryptocurrencies. It makes distinctions between the U.S. dollar and foreign currency (taxed as property rather than currency). Currently, cryptocurrency is taxed as property under U.S. tax laws, making transactions and appreciations in value subject to income and capital gains taxes. The report acknowledges that the current tax structure could freeze investment and exploration into new virtual currencies, especially for smaller transactions such as coffee purchases (people apparently really want to buy coffee with cryptocurrency). Congressional representatives Schweikert and Polis introduced a bill proposing a solution – the Cryptocurrency Tax Fairness Act of 2017 – that would exempt taxation for virtual currency purchases under $600. The bill has yet to become law, but the report estimates that as virtual currencies continue to become more popular, more bills on the topic will be introduced.
The report discusses the issue of transmitting money for virtual currency, and that it currently could require money transmitters to obtain licenses to operate separately in every U.S. state (except Montana). The report presents solutions, such as the Uniform Law Commission, a nonpartisan commission to create consistent state laws that could draft and approve legislation that would clearly and uniformly define what virtual currency businesses need to file to become money transmitters. However, that solution could take years for the legislation to be enacted in all U.S. states. The report encourages Congress to look at many solutions to this problem, and will present a rigorous cost-benefit analysis. As a side note, money transmitting for virtual currency is incredibly important to allow mass-adoption of cryptocurrency. It is often difficult to transfer fiat money into cryptocurrency. There are many steps involved in the process, and it can be slow, technical, challenging, and uncertain. Finding a good solution to the money transmission problem is going to be a major step in opening the cryptocurrency market, bringing down barriers of entry, and increasing market-place demand.
The report encourages Congress to find solutions that balance the needs of consumer protection, security, and entrepreneurship. It pushes for a common and coordinated regulatory framework that creates clarity in the industry. It recommends regulations that are not overly prescriptive or constraining, so blockchain technology will be allowed to reach its full potential.
The conclusion on pages 225 and 226 makes four recommendations:
Policymakers and the public should become more familiar with digital currencies and other uses of blockchain technologies, which have a wide range of future application. Regulators should continue to coordinating with each other to guarantee coherent policy frameworks, definitions, and jurisdictions. Policymakers, regulators, and entrepreneurs should work together to ensure developers can quickly deploy blockchain technology to protect Americans from fraud, theft, and abuse, while ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. Government agencies at all levels should consider and examine new uses for blockchain technology to help make the government function more efficiently.
Overall, this is an enormously positive endorsement from the U.S. Congress. We will likely see cryptocurrency and blockchain technology flourish throughout the United States. It is a bright future for Americans involved in blockchain technology and the cryptocurrency marketplace.
LargeSnorlax on March 19th, 2018 at 20:45 UTC »
More accurately, it mentions the use of Blockchain more than Cryptocurrencies - Which is already being used in early stages by banks, governments and businesses around the world, not so much Crypto.
This statement is most telling:
The report shows Bitcoin’s limitations as a medium of exchange, citing long transaction times and high fees, and further acknowledging that protocol improvements and off-chain solutions could speed up processing times and reduce transaction fees to help move cryptocurrency into the realm of actual currency.
A cryptocurrency must do 3 things to compete as an actual currency, vs things like Debit, Credit Cards and Cash:
It must be able to transact in seconds, the equivalent of grabbing a couple of bills out of your pocket, or pulling out a card in order to make a transaction It must be cheap - Preferably cheaper than your average credit card transaction (for both Merchant and you) It must be secure and immutableThere are a few Cryptos which tick a few of these boxes, but none yet that tick all of them. A real currency and medium of exchange needs to do all 3 in order to compete and beat the current competition.
Whichever one does this, expect slow, but widespread adoption. Merchants are always looking for ways to make more money, and if a Cryptocurrency gives them this option, they will grab it.
Infinite101 on March 19th, 2018 at 20:29 UTC »
Until crypto slides again and we see the “governments are trying to destroy us” posts tomorrow.
stevoli on March 19th, 2018 at 20:14 UTC »
Well, the government says it's mainstream, so I guess it's mainstream.